- This event has passed.
Noggins @ Hosford PPS! (1)
WHAT: Noggin @ Hosford Middle School
WHERE: Online (link to be shared with volunteers) & LIVE @ Hosford Middle School, 2303 SE 28th Pl, Portland, OR 97214
WHEN:
1. Thursday, May 27, 9:30am – 12:30pm Pacific (Virtual)
We did it!
Hosford, Hippocampi & Hope
2. Friday, May 28, 9:30am – 12:30pm Pacific (Virtual)
3. Thursday, June 3, 2:00 – 4:00pm Pacific (LIVE @ Hosford, 2303 SE 28th Pl, Portland, OR 97214)
4. Friday, June 4, 2:00 – 4:00pm Pacific (LIVE @ Hosford, 2303 SE 28th Pl, Portland, OR 97214)

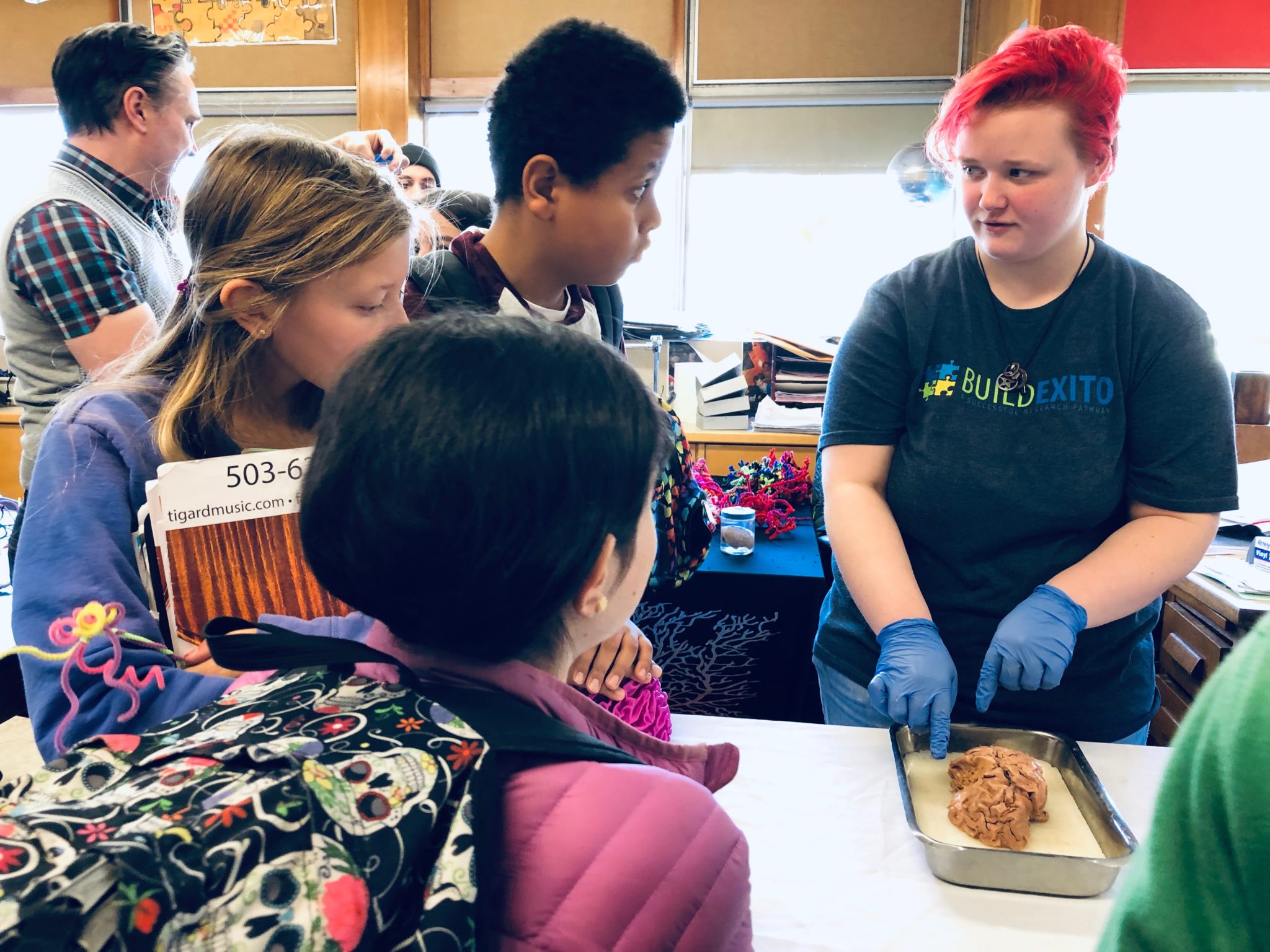
We are thrilled to return to Hosford, and hear what middle school biology students are learning about energy (ATP!) and brains!

We’ll gather virtually on Thursday (5/27) and Friday (5/28) to meet, discuss neuroscience research and introduce a found object brain cell project. We’ll be back LIVE on both Thursday (6/3) and Friday (6/4) to see all the neurons and glial cells, consider more questions and hold a few extra brains!
COMMITTED PARTICIPANTS
1. Bill Griesar, NW Noggin/PSU/OHSU
2. Jeff Leake, NW Noggin/PSU
3. Magda Armendariz Sullivan, PSU
4. Kass Fitzgerald, PSU
5. Alex Heinrich, PSU
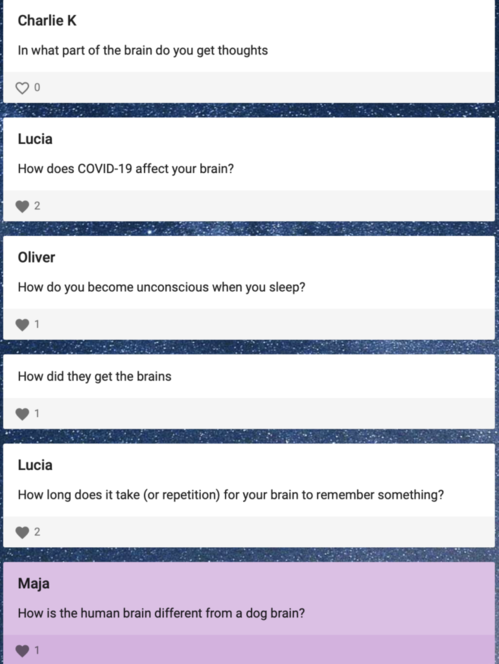
Student Questions!
In what part of the brain do you get thoughts?
How does COVID-19 affect your brain?

“While primarily a respiratory disease, COVID-19 can also lead to neurological problems. The first of these symptoms might be the loss of smell and taste, while some people also may later battle headaches, debilitating fatigue, and trouble thinking clearly, sometimes referred to as “brain fog.” All of these symptoms have researchers wondering how exactly the coronavirus that causes COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2, affects the human brain. In search of clues, researchers at NIH’s National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) have now conducted the first in-depth examinations of human brain tissue samples from people who died after contracting COVID-19. Their findings…suggest that COVID-19’s many neurological symptoms are likely explained by the body’s widespread inflammatory response to infection and associated blood vessel injury—not by infection of the brain tissue itself.”
LEARN MORE: Taking a Closer Look at COVID-19’s Effects on the Brain
How do you become unconscious when you sleep?
How did they get the brains

LEARN MORE: A BioGift of Brains
How long does it take (or repetition) for your brain to remember something?
How is the human brain different from a dog brain?
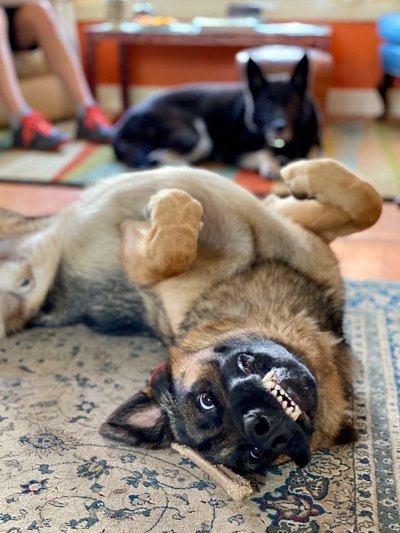

“…we can see from an MRI of a dog brain that even though it is smaller than a human brain, all of the same basic structures are present. This is true for large regions like the cerebral cortex and the cerebellum, as well as for smaller, subcortical structures like the brainstem, hippocampus, amygdala, and basal ganglia, which have important roles in movement, memory, and emotion.
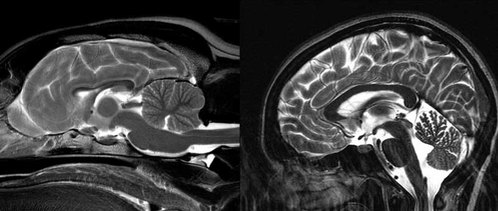
“Dogs also have large olfactory systems, comprising about two percent of the total brain weight (compared to 0.03 percent in humans). Where dogs fall short is in the cortex. Apart from being smaller, there are fewer folds, which means less surface area and fewer neurons. The frontal lobe, which in humans occupies the front third of the brain, is relegated to a paltry ten percent in dogs…”
LEARN MORE: Decoding the Canine Mind
“While ferret, mongoose and cat have increasingly larger cortices (3.1 g, 9.3 g, and 24.2 g) with increasingly more neurons (39 million, 116 million, and 250 million neurons, respectively), we find that the lion has approximately as many neurons in the cerebral cortex as the average found in dogs, ca. 500 million neurons, despite a twice larger cortex in the lion than in the dogs…Remarkably, of all the individuals we analyzed, the one with the most neurons in the cerebral cortex was a golden retriever dog (627 million neurons), followed by the lion (545 million neurons), one of the raccoons (512 million neurons), the striped hyena (495 million neurons), a smaller dog of unspecified breed (429 million neurons) and a second raccoon individual (395 million neurons).“
LEARN MORE: Dogs Have the Most Neurons, Though Not the Largest Brain
What happens in your brain when you learn something new?
what’s the worst thing that could happen to the brain
Are you your brain or are you you
When did we start wondering how the brain worked?
LEARN MORE: Why Study the History of Neuroscience?
What happens in your brain when you associate color with flavor? Like a yellow jelly bean tastes or is associated with lemon.
What are the wrinkles?
How much of our brain do we actually consciously know how to use?
why can some people daydream in almost like full movies but some people cant?
Do we really only use 10% of our brains?
hOW does it WOORKK?
why do i get migraines and what causes them to be clusters or every month?
How does your brain process words so fast? How can you be saying something at the same time that your brain is trying to figure out what to say?
why do some people like me believe in fixed mindsets while others don’t
How come my autism makes it hard to process my words?
does our brain actually get bigger when we get smarter?
How do brains grow bigger?
How do the conscious mind, and the unconscious mind relate when you remember your dream?
what makes you forget things
What is the biggest mystery about the brain at the moment? What would you say is the biggest discovery about the brain?How does the brain use energy?When is the brain fully developed?
how can your emotions effect different parts of your brain, like creativity or decision making.
How effective is sleep on your brain?
can your brain actually grow in size?
Does the Brain change when your mental health is different???
How big can a brain get? and what is the heaviest brain ever recored?
I wonder how different peoples brains are different?
what do brainzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzz taste like
can the size of your brain affect how smart you are?
What does your brain look like as you get older and how much does it evolve over 10 years of your life?
DOES YOUR BRAIN ACTUALLY FART WHEN YOU CANT REMEMBER SOMETHING?????
Why does the brain have all of those wrinkles?

How does the brain change over time? How do other people’s reactions to things we do/say affect our brain? How are different people with different mindsets, backgrounds, and life choices brains are different? Are people with bigger brains necessarily smarter? How much of something harmful is needed to impact your brain? Are some people’s creative and logical brain halves switched, and how would that affect them?
If you don’t have the creative part of your brain will it just completely stop working?
How much memory can a brain hold?
How does the brain work when you are in a coma?
How does the brain change as we grow up?
does/how does our brain stay awake while we sleep?
Why do you control the right side of your body with the left side of your brain and the other way around.
How do external factors reach the processing center of the brain, and can you simulate external things?
is there a limit to how much knowledge we can hold
why do we dream? i also would just like to learn more about the brain in general
How do different parts of our brain know where to control things and how to do it, because different parts of the brain are used for different things, so how does the brain itself know the difference?
Also, maybe, what is the physical brain like.
Why and how do we dream?
is the brain one part or is it two parts that are connected?
how much of your energy does the brain use up
How much oxygen does the brain need to stay conscious?
Why and how do we dream? How/why do we have different types of dreams?

SEE WHAT WE’VE DONE BEFORE @ HOSFORD!
Honest selves @ Hosford

Brains, Art & Inquiry @ Hosford

High energy Hosford: Tumors, music & drugs!